With the rapid adoption of Generative AI in enterprise environments, the technology for effectively processing unstructured data, such as vast amounts of internal corporate documents, is emerging as a core competitive advantage. For enterprise AI solutions, accurate document recognition and semantic understanding are key determinants of success.
In response to these market demands, the hifenn (formerly Raon Assistant) team has developed ‘DEEP SCAN,’ an advanced document preprocessing engine. Today, we will conduct an in-depth examination of the operating principles and differentiating strengths of this core technology.
DEEP SCAN: A New Paradigm in Document Recognition
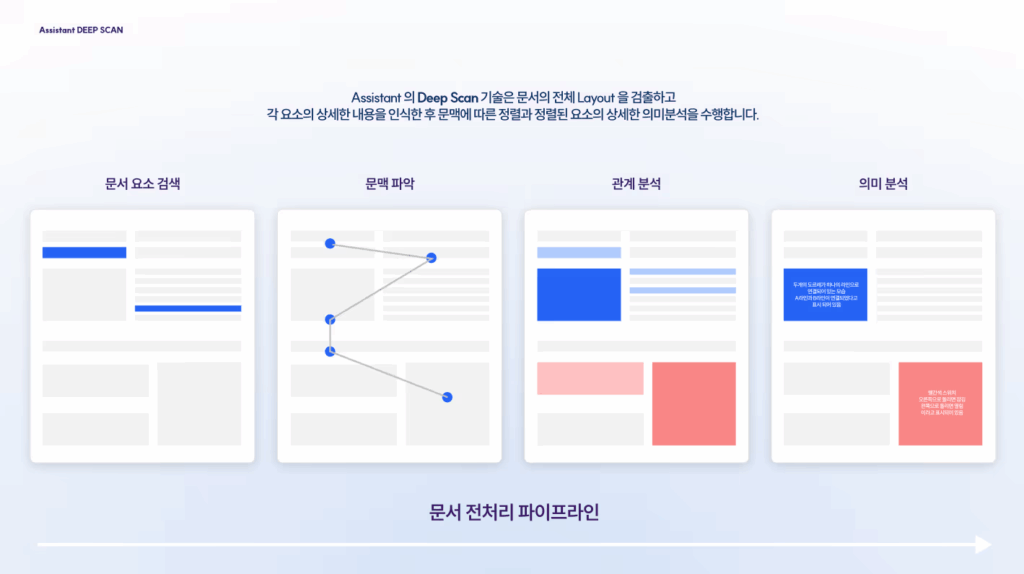
DEEP SCAN is hifenn’s core engine that goes beyond simple OCR or text extraction technology to understand the structure and context of a document. This technology handles Document Data Preprocessing within the AI Assistant Service Pipeline, accurately recognizing and analyzing the structural form and content of unstructured documents, and converting them into a format optimized for AI-based search and generation.
“Based on a character detection model with an average recognition rate of over 97% for both Korean and English, it understands the overall document layout and analyzes the relationship between each element.”
DEEP SCAN’s Position: The Core Pillar of the AI Pipeline
DEEP SCAN plays a pivotal role in hifenn’s overall AI service pipeline:
- Data Collection (ETL)
- Gathers data from various sources within the enterprise, including MS Graph, ERP, Databricks, and Airflow.
- Unstructured data is channeled into a structured pipeline.
- Document Preprocessing (DEEP SCAN)
- Structural Documents (Table): Accurate interpretation of table and spreadsheet data.
- Documents with Images: Analysis of visual materials such as charts, graphs, and photos.
- Manual Images: Specialized layout processing for technical documents or guides.
- General Images: Interpretation of various forms of image content.
- Data Orchestration: Context-based reconstruction of extracted information.
- Time-Series Data (in development): Analysis of time-based data.
- Multimedia Data (in development): Processing of video/audio content.
- Structural Documents (Table): Accurate interpretation of table and spreadsheet data.
- Vector Search
- Converts the preprocessed data into a searchable format using BM25, MMM, and Ensemble techniques.
- Converts the preprocessed data into a searchable format using BM25, MMM, and Ensemble techniques.
- Vector Indexing
- Optimizes search efficiency with advanced algorithms such as HNSW and Cognitive.
- Optimizes search efficiency with advanced algorithms such as HNSW and Cognitive.
DEEP SCAN acts as the bridge connecting ETL and Vector Search, which are the most complex and technically challenging parts of the pipeline. The process of converting various types of unstructured documents into structured data that AI can understand happens here.
The Three Core Technologies of DEEP SCAN
1. Intelligent Document Element Recognition (Document Detection)
DEEP SCAN’s most fundamental yet innovative function is its ability to accurately recognize all constituent elements of a document. It utilizes a high-performance detection model boasting an average recognition rate of over 97% for Korean and English.
Of particular note is its ability to go beyond simple character recognition to understand the overall document layout and identify the relationships between the elements. This allows for the precise analysis of complex technical documents and manuals.

2. LLM-based Image Semantic Analysis (Visual Context Understanding)
DEEP SCAN’s second differentiator is that it doesn’t merely extract images contained within a document; it performs an in-depth analysis of their meaning. It leverages the latest LLM (Large Language Model) technology to convert the content of images into text and link it to the document’s overall context.
This technology enables documents containing charts, diagrams, sketches, and technical drawings—previously impossible to search—to become targets for text-based retrieval. This is a core technology that significantly enhances the usability of technical manuals and design documents used in real industrial settings.

3. Contextual Data Orchestration
The most innovative aspect of DEEP SCAN is its ability to reconstruct all extracted information according to the document’s original context. It goes beyond recognizing characters or images to grasp the meaning and relationships each element holds within the document, organizing the data accordingly.
For example, it connects table data, its explanatory text, and related images into a single semantic unit, allowing the AI to understand the document in a way similar to a human. This is the foundational technology that enables true meaning-based search and Q&A that goes beyond simple keyword matching.
The Data Orchestration process is achieved through the following steps:
- Completion of individual processing for all document elements.
- Analysis of relationships between elements and composition of semantic units.
- Reconstruction of the hierarchical document structure.
- Contextual information enhancement and metadata addition.
DEEP SCAN’s Innovative Processing Process
The 6-Step Intelligent Document Processing Pipeline
DEEP SCAN operates through a meticulously designed 6-step pipeline to process complex documents. Each stage is independent yet organically connected, leading to accurate and meaningful document analysis results.
1. Contents Loader
The starting point of the entire process, efficiently loading documents in various formats (PDF, Word, Image, etc.) into the system. Basic metadata and format information are also collected here.
2. Layout Analysis
AI-based algorithms analyze the overall structure of the document. This critical stage identifies areas like headers, footers, body text, and sidebars, grasping the logical document structure. Its value is particularly significant for complex multi-column layouts or documents with non-standard designs.
3. Element Detection
Based on layout analysis, individual elements within the document (text blocks, tables, images, shapes, etc.) are precisely identified. This process evaluates not only the element type but also the relationship and importance of each element.
4. Intelligent OCR Processing
General text is processed by a high-performance OCR engine, and table data is analyzed with specialized algorithms:
- Text Recognition: Optimized for multi-language support and special character processing.
- Table Processing: Table area extraction (Crop) → Row/Column structure analysis (Segmenting) → Cell data extraction → Relationship reconstruction.
5. Image Analysis
All images within the document are analyzed in depth using the latest computer vision and LLM technologies:
- Image type classification (photo, chart, diagram, sketch, etc.).
- Text recognition and processing within the image.
- Semantic-based caption generation and metadata extraction.
- Analysis of relevance to the document context.
6. Merge & Re-order
The final stage integrates all analysis results and reconstructs them based on meaning:
- Merging related text blocks and sorting logical order.
- Setting relationships between tables, text, and images.
- Reordering elements according to the document’s logical flow.
- Structuring metadata optimized for search and Q&A.
Game Changer in the Industry: DEEP SCAN Use Cases
1. Realizing Work Automation through Accurate Data Extraction
- Intelligent Extraction and Processing of Table Data
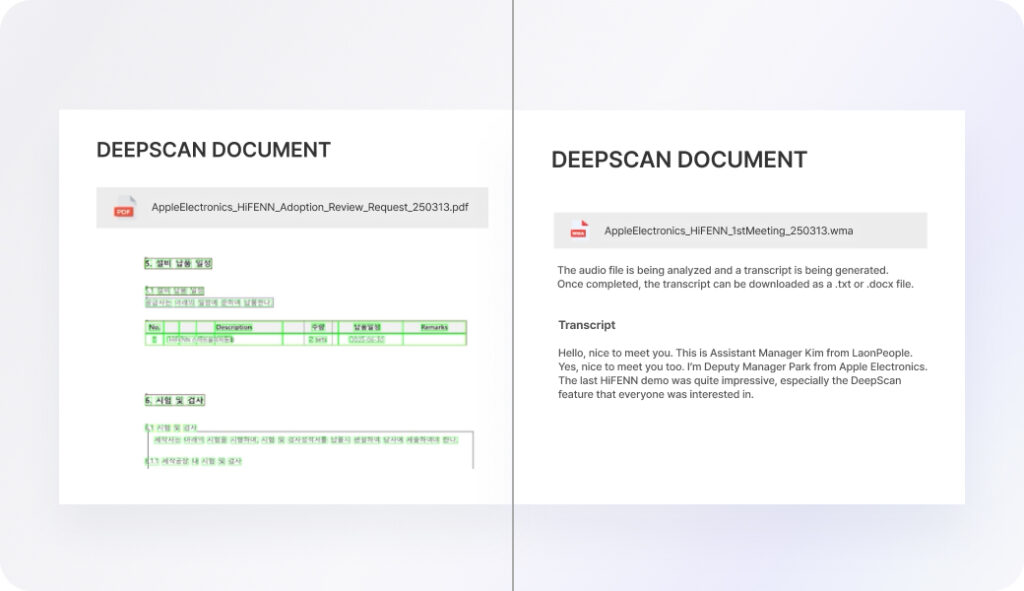
DEEP SCAN’s table recognition technology enables the automation of data-centric tasks such as ERP data entry or financial document processing. It accurately recognizes information in table form, even when it appears as plain text, and converts tables stored as images into structured data.
“Previously, we manually digitized hundreds of pages of financial statements. After adopting DEEP SCAN, processing time was reduced by 97%.” (Case study from a financial institution user)”
2. Providing Accurate Search through Context-Based Information Reconstruction
- Semantic Document Interpretation, Not Just Location
DEEP SCAN reconstructs information based on the logical relationship (TO-BE) between document elements, rather than their physical position (AS-IS). This delivers exceptional performance, especially when processing technical documents or contracts with complex layouts.
In actual use cases, this context-based processing improved search accuracy from 85% to 97%, allowing users to find the information they need faster and more accurately.
3. Utilizing Information within Images and Diagrams
- Expanding Search Scope by Datafying Visual Materials
The biggest limitation of conventional document processing systems was their inability to utilize information contained within images or diagrams. DEEP SCAN overcomes this by recognizing image-form tables, charts, and graphs and converting their content into structured data.
In a case study involving a manufacturer’s technical manual, automatically recognizing and connecting diagrams and parts lists allowed for the instant retrieval of specific component information within thousands of pages of documents.
4. Implementing Multimodal Search with Intelligent Image Captioning
- Image Analysis That Understands Beyond What It Sees
One of DEEP SCAN’s most innovative features is its captioning capability, which analyzes the meaning of images within a document and describes them in text. This goes beyond simple image tagging to a level of understanding and explaining the image’s content and context.
This technology allows users to search using image content, such as “control panel with a red switch,” or to include visual elements in their query, such as “diagram with two connected pulleys.”
#AI #Enterprise #Architecture #TechnicalDeepDive