What if there was an AI that could understand images and learn autonomously without the need for labeling?
Today, we delve into Meta’s Vision AI model: DINOv3.
DINOv3 is a vision model based on Self-Supervised Learning, which means it learns visual patterns autonomously without human-applied labels. It demonstrates powerful versatility, usable for various visual tasks after just a single training session, and is gaining attention in the industry as a model that “changed the paradigm of image recognition.”
Let’s now examine how DINOv3 learns by itself, meticulously understands images, and how it can be utilized in real industrial settings.
1. Self-Supervised Learning – AI That Finds Patterns Autonomously Without Labels
When we typically teach AI, we go through a process where humans manually attach explanations (labels), such as “This photo contains a cat.” However, Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) refers to a method where AI finds patterns autonomously without this tedious labeling.

In essence, the AI creates its own learning criteria by comparing “which parts of this image are similar, and which parts are different.” This allows it to learn from a massive amount of unlabeled images across various domains like the internet, satellite imagery, medical scans, and industrial sites, without human intervention.
The DINO series is a representative model of SSL. DINOv3, in particular, has been expanded to a much larger scale than its predecessors, trained on a staggering 1.7 billion images. Because it has been trained on such a large volume of unlabeled data, it is not confined to a specific domain and can demonstrate excellent generalization performance across diverse image domains.
As a result, DINOv3 is seen as the “AI that understands the world’s patterns without labels,” taking a significant step closer to human-like Visual Intelligence.
2. Vision Foundation Model – A Universal Model That Works Everywhere with a Single Training
Just as having a strong foundation in math, science, and language allows us to apply that knowledge to various fields in school, a Foundation Model is a model equipped with the fundamentals to excel at a wide range of visual tasks, not just solving one specific problem.
A model with such fundamentals can adapt immediately to new problems without having to learn from scratch. DINOv3 was developed precisely with this goal in mind: to be a ‘Vision Foundation Model.’
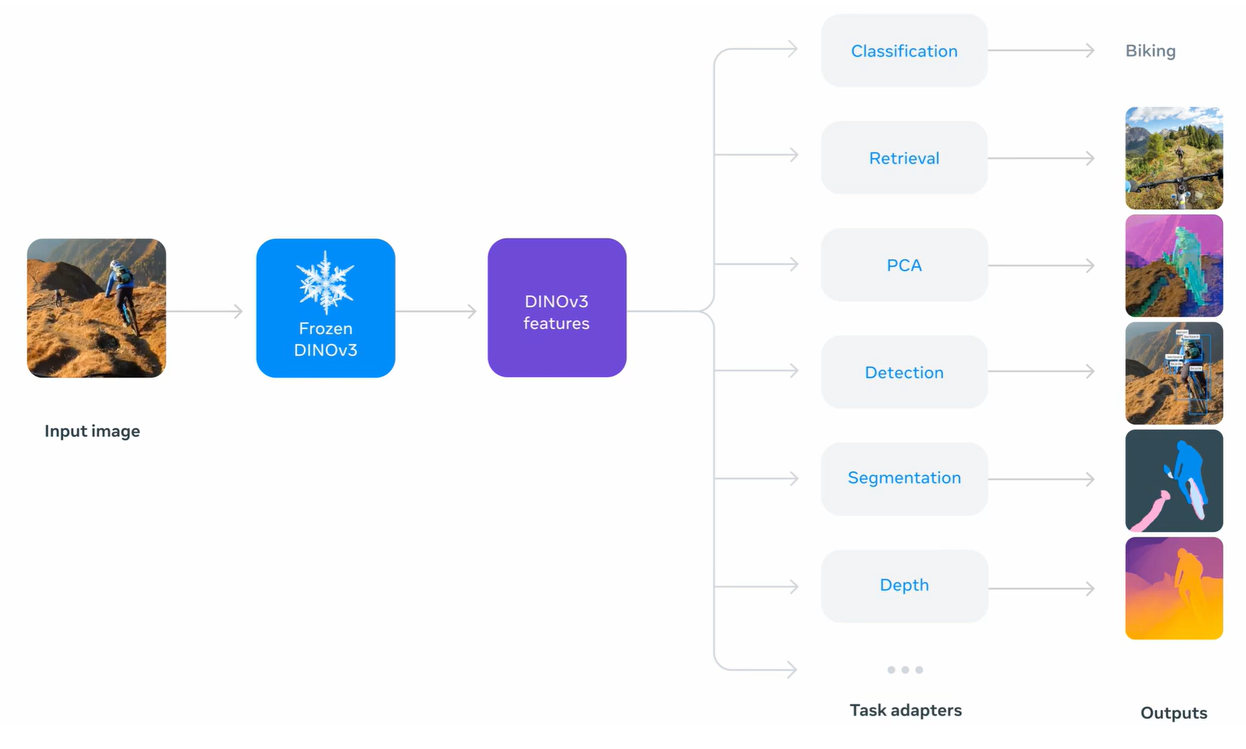
Once trained, it can perform various tasks without additional fine-tuning:
- Classification — Identifying what objects are in an image.
- Segmentation — Delineating object boundaries at the pixel level.
- Object Detection — Locating the position and type of objects in an image.
- Video Tracking — Following the movement of objects over time.
While previous-generation models required separate fine-tuning for specific tasks, DINOv3 delivers strong performance across various settings without such adjustments. It marks a step closer to true general-purpose visual AI.
3. Dense Feature Alignment The Secret to ‘Meticulously Understanding the Whole Picture’: Gram Anchoring
When AI looks at an image, simply understanding “This is a cat” has limitations. A truly smart model must also understand the meaning of every part (pixel, patch) in the picture. The information extracted precisely across the entire image is called ‘Dense Features’ (fine-grained features).
Ironically, when models are scaled up and trained for a very long time, this fine-grained quality can blur. In other words, the subtle distinctions collapse, leading to a tendency to view the image in an overly generalized way.

DINOv3 addresses this by introducing a new regularization step called Gram Anchoring. This technique uses the similarities between multiple patches within an image as a reference point (Anchor), helping to maintain a consistent relationship between patches even during training.
Thanks to this, DINOv3 can produce cleaner and more stable similarity maps, even with high-resolution images. As a result, it shows much better performance in detailed visual tasks such as Depth Estimation, 3D Correspondence, and precise Object Segmentation.
4. DINOv3 Model Architecture – A Familiar Yet Robustly Refined Design
Looking at the structure of DINOv3, it is not a completely new invention but rather a model that intricately combines and stabilizes various techniques proven effective in the past. In other words, the components are familiar, but the assembly is far more robust.
1. Backbone — Flexible Design Spanning ViT and ConvNeXt
DINOv3 supports not only the Vision Transformer (ViT) but also the ConvNeXt family as its base network (Backbone). This design considers the diversity of research and industrial/deployment environments, allowing for flexible utilization even in situations with limited GPU resources. Pretrained weights are already available on official hubs and GitHub, enabling developers to apply them to various tasks.
2. Self-Distillation — Stable Learning through a ‘Student-Teacher’ Structure
DINOv3 uses both a Student and a Teacher network during training. The Student learns by viewing various cropped images (different views and resolutions), and the Teacher smoothly follows the Student’s parameters using EMA (Exponential Moving Average). In this process, the Teacher provides a stable goal (soft target), and the Student mimics that goal, learning increasingly robust representations. Ultimately, the knowledge is distilled from the large 7B parameter Teacher model into a smaller Student model, resulting in a structure that achieves both performance and efficiency.
3. Multi-Crop Strategy — Visual Flexibility Learned from Diverse Views
It employs a Multi-Crop Strategy, cutting the same image into multiple resolutions and views (global/local crops) for training. This grants the model the expressive power to recognize the essence of an object regardless of size or viewpoint. DINOv3 essentially teaches itself the visual sense to “recognize the same object whether viewed from afar or up close.”
4. Masking & Self-Prediction — Predicting the Unseen Autonomously
DINOv3 also utilizes the Self-Prediction technique in the style of iBOT. It involves masking some patches of the image and using the remaining information to predict the hidden parts. Through this process, the model develops a deep understanding of the image structure and context.
In summary, DINOv3 is less “new” and more “close to a complete design.” It is a Vision Foundation Model that intricately weaves proven elements together to maximize stability, efficiency, and generalization.
5. Utilizing the DINOv3 Model – Fast Prototyping and Practical Use, Even with Few Labels
DINOv3 is more than just a research model; it is designed as a “universal visual engine that can start quickly even in real-world environments with scarce labels.” This means that a powerful vision-based AI can be rapidly prototyped with only a small amount of data.
1. A Strong Starting Point in Few-shot / Low-Label Environments
DINOv3’s key strength lies in the extremely high expressiveness of its pretrained backbone. Therefore, without needing to retrain the entire model, one can freeze the backbone and add only a thin head (e.g., linear classifier, MLP) to achieve excellent performance in various tasks like Classification, Segmentation, and Depth Estimation. Thanks to the improved Dense Feature quality, it is highly advantageous for precise visual tasks requiring pixel-level distinction, such as Segmentation and 3D matching.
2. Production Considerations – Wide Selection from Edge to Server
DINOv3 was designed with actual deployment environments in mind. The available model families are diverse:
- ViT Series: Small / Base / Large / Huge+
- ConvNeXt Series: Tiny ~ Large
This means that a model appropriate for the situation can be easily selected and deployed, ranging from edge devices (lightweight environments) to server-grade GPUs (high-performance environments).
3. Perfect Integration with the Open-Source Ecosyste
DINOv3 is fully integrated with major open-source platforms, including PyTorch Hub, Hugging Face Transformers, and GitHub. This allows developers to:
- Extract embeddings immediately (Feature Embedding)
- Experiment with combinations with other models (e.g., CLIP, SAM, etc.)
- Instantly load official example code + pretrained weights
In short, DINOv3 can be called a “practical vision model that can be used immediately without labels,” from research experiments to industrial prototyping.
Conclusion – The Direction of ‘Self-Learning Visual Intelligence’ Shown by DINOv3
DINOv3 is not just “another new model.” It is a landmark demonstrating the evolution of Visual Intelligence—AI that understands the visual world autonomously without human intervention.
DINOv3’s ability to learn from billions of unlabeled images and immediately adapt to diverse tasks such as classification, segmentation, and 3D perception after a single training session suggests the arrival of an era where AI observes and interprets the world in a way closer to humans.
Now, based on Foundation Models like DINOv3, we are entering a ‘high-efficiency AI development era’ where we can:
Quickly prototype even with minimal data, and Solve real-world problems.